Understanding the Different Types of Eczema and Their Causes

Introduction
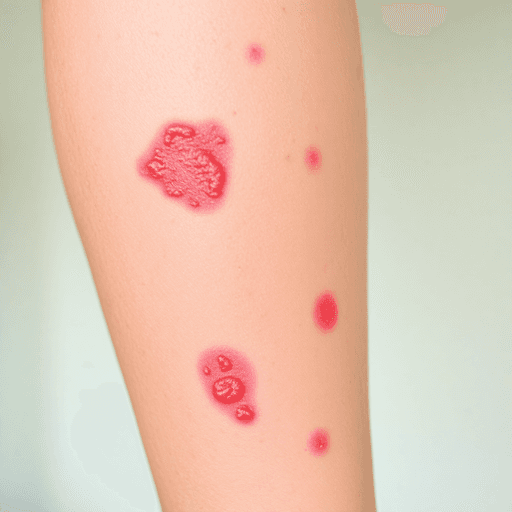
Eczema is a common skin condition characterized by inflammation, redness, and irritation. It encompasses several types, each with unique symptoms and causes. Understanding the different types of Eczema and their causes is crucial for effective management and reducing discomfort. From atopic dermatitis to dyshidrosis, each type has its own triggers that may include genetic factors, environmental influences, or allergens.
Comprehending these distinctions can significantly aid in managing flare-ups and maintaining skin health. Treatment options vary but typically involve lifestyle adjustments, topical treatments, and sometimes phototherapy. Recognizing the specific kind of Eczema you have can guide you toward appropriate therapies and improve quality of life. By delving deeper into the nuances of this condition, you equip yourself with the knowledge needed to tackle Eczema effectively.
What is Eczema?
Eczema is a common skin condition that causes inflammation, leading to redness and irritation. It appears as dry, itchy patches on the skin that can vary in severity and location. Eczema affects each person differently, with some experiencing mild discomfort while others may have severe inflammation that requires medical attention.
Distinction from Other Skin Conditions
While the terms Eczema and dermatitis are often used interchangeably, there is a difference between them. Eczema usually refers to a chronic condition with recurring symptoms, whereas dermatitis can refer to any inflammatory skin response.
Common symptoms of Eczema include:
- Redness
- Itching
- Dry or scaly patches
- Swelling
By understanding the specific signs of Eczema, we can differentiate it from other skin conditions. This knowledge is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment. To effectively manage Eczema, it is important to identify its symptoms and triggers in order to develop personalized care strategies.
1. Atopic Dermatitis (Atopic Eczema)
Atopic Dermatitis, commonly known as atopic Eczema, is the most common type of Eczema. It is a long-lasting condition characterized by inflamed, itchy skin and can affect various parts of the body such as the face, elbows, knees, and arms. It usually begins in childhood but can continue into adulthood or develop later in life.
Common Symptoms:
- Itchy Skin: An intense itch that may become unbearable, leading to scratching and further irritation.
- Redness and Swelling: The affected areas often become red and swollen due to inflammation.
- Dry and Scaly Skin: The skin tends to become dry, leading to scales or crusting over time.
- Thickened Skin: Prolonged scratching can cause the skin to thicken in affected areas.
Causes
Understanding the causes of atopic dermatitis is essential for effective management. Key contributors include:
- Genetic Factors: A family history of Eczema, allergies, or asthma often increases susceptibility. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in the development of eczema atopic dermatitis.
- Environmental Triggers: Common triggers like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or certain foods can exacerbate symptoms. Environmental factors such as humidity levels and exposure to irritants or allergens also contribute significantly.
By recognizing these symptoms and causes, individuals can better manage their condition through targeted treatments such as those offered in our Eczema Treatment range that includes creams and body washes suitable for all ages. Additionally, making lifestyle adjustments can further help in managing this condition effectively.
2. Contact Dermatitis (Allergic & Irritant Contact Dermatitis)
Contact dermatitis is a type of Eczema that occurs when the skin reacts to substances it encounters. It is categorized into two main subtypes: allergic contact dermatitis and irritant contact dermatitis.
1. Allergic Contact Dermatitis
This form results from an allergic reaction to a substance, known as an allergen, which the body identifies as foreign. Upon exposure, the immune system sensitizes and reacts within 48 hours, leading to skin inflammation. Common allergens include:
- Nickel
- Latex
- Fragrances
- Certain preservatives found in cosmetics and skincare products
2. Irritant Contact Dermatitis
Unlike its allergic counterpart, this type arises from direct damage to the skin's outer layer by a chemical or physical irritant. The response is usually immediate. Frequent culprits involve:
- Soaps and detergents
- Cleaning agents
- Solvents
- Industrial chemicals
Symptoms of contact dermatitis often manifest as redness, itching, and blistering at the site of contact. Identifying specific triggers is crucial for prevention and management, highlighting the importance of understanding the various types of Eczema and their causes.
3. Dyshidrotic Eczema (Pompholyx)
Dyshidrotic Eczema, also known as pompholyx, is characterized by small, fluid-filled blisters that mainly affect the hands and feet. These blisters can be quite painful and are often accompanied by itching or burning sensations. As the condition worsens, the skin around these blisters may become dry and flaky.
Common Triggers of Dyshidrotic Eczema
Several factors can trigger dyshidrotic eczema flare-ups:
- Metals: Contact with metals such as nickel and cobalt is a common trigger. Individuals sensitive to these metals may experience worsening symptoms after exposure.
- Stress: Emotional stress is another significant trigger for dyshidrotic Eczema. High stress levels can exacerbate the condition, leading to an increase in blister formation.
- Damp Conditions: Prolonged exposure to moisture or damp environments may also contribute to flare-ups. This includes working in wet conditions or frequent handwashing without proper drying.
Understanding these triggers is crucial for effectively managing dyshidrotic Eczema. Identifying and avoiding specific triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of episodes, improving overall comfort and skin health.
4. Nummular Eczema (Discoid Eczema)
Nummular Eczema, also known as discoid Eczema or papular Eczema, is a distinct form of Eczema characterized by its unique coin-shaped spots on the skin. These lesions are often itchy and inflamed, presenting themselves as circular patches that can appear on various parts of the body. Unlike other kinds of Eczema, nummular Eczema does not typically exhibit the widespread dryness seen in conditions like atopic dermatitis.
Connection Between Nummular Eczema and Dry Skin
The connection between nummular eczema flare-ups and dry skin conditions is particularly significant. Individuals with naturally dry skin or those exposed to harsh environmental conditions may notice an increase in these round patches during colder months when humidity levels drop. The skin's inability to retain moisture can exacerbate the condition, leading to more frequent occurrences.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Nummular Eczema
Commonly mistaken for ringworm due to its appearance, nummular Eczema requires careful observation and diagnosis. Treatment often involves maintaining proper skin hydration through emollients and topical medications designed to reduce inflammation and itchiness. Understanding the triggers and maintaining a routine that prioritizes skin moisture can play a crucial role in managing this form of Eczema effectively.
5. Seborrheic Dermatitis (Seborrheic Eczema)
Seborrheic dermatitis, a common type of Eczema, often appears in areas with a high concentration of oil-producing glands, especially the scalp and face. What sets this condition apart is its preference for oily skin areas, which contributes to its distinctive symptoms.
Key Symptoms
- Dandruff-like Flakes: One of the most recognizable signs, these flakes can range from white and powdery to yellowish and greasy.
- Redness and Itching: Affected areas may experience persistent redness and itching, often worsened by stress or changes in weather.
- Scaly Patches: These patches can appear not only on the scalp but also on other oil-prone areas like the eyebrows, sides of the nose, and behind the ears.
Potential Triggers
Understanding the triggers of seborrheic dermatitis can aid in managing this type of Eczema effectively. Factors such as hormonal changes, cold or dry weather, and specific skincare products might contribute to flare-ups. Although the exact cause remains unclear, it is suspected that an overgrowth of a yeast called Malassezia on the skin could play a role.
Recognizing these characteristics helps distinguish seborrheic dermatitis from other types of Eczema, guiding effective management strategies tailored to its unique symptoms.
6. Neurodermatitis (Lichen Simplex Chronicus)
Neurodermatitis, also known as lichen simplex chronicus, primarily develops from a continuous cycle of itching and scratching. This condition usually affects specific areas of the skin, resulting in thickened, leathery patches due to repeated rubbing or scratching. These patches can occur on the neck, scalp, shoulders, wrists, ankles, and even genital areas.
The itching sensation is often severe and may be triggered by stress, anxiety, or other psychological factors. People with neurodermatitis might find themselves scratching unconsciously, particularly during times of increased emotional distress.
Key characteristics of neurodermatitis include:
- Chronic Itching: The main feature of neurodermatitis is an urge to scratch that often gets worse at night.
- Thickened Skin: Ongoing scratching leads to thickened patches that may become scaly or discoloured over time.
- Psychological Triggers: Stress and anxiety are common factors that worsen the urge to scratch.
Treating neurodermatitis often involves breaking the itch-scratch cycle through behavioural interventions and addressing any underlying psychological issues. Understanding these factors can help manage this difficult type of Eczema effectively.
7. Stasis Dermatitis (Venous Eczema)
Stasis dermatitis, also known as venous Eczema, occurs in people with poor circulation, especially in the lower legs. This condition is closely related to chronic venous insufficiency, where weakened veins have difficulty sending blood back to the heart. As a result, fluid leaks from the veins into nearby tissues, causing discomfort and visible changes in the skin.
Symptoms of Stasis Dermatitis Include:
- Swelling: A common sign of stasis dermatitis is swelling in the lower legs and ankles, often getting worse throughout the day.
- Redness and Discoloration: The affected areas may appear red or brown, indicating inflammation and blood pooling.
- Itching and Irritation: Persistent itching can lead to further skin damage through scratching, making the condition worse.
- Scaling and Crusting: The skin may become dry, flaky, or crusty as the condition progresses.
This type of Eczema requires careful management to relieve symptoms and prevent complications like ulcers. Improving circulation through compression stockings or elevating the legs can be helpful for those dealing with this difficult form of Eczema.
Common Causes Behind Different Types of Eczema
Eczema is a complex condition with various types, each rooted in distinct causes. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective management and prevention. Here are some common factors that contribute to the development of different types of Eczema:
1. Genetic Factors
Eczema often runs in families, indicating a genetic predisposition. Individuals with a family history of Eczema, asthma, or hay fever are more susceptible to developing atopic dermatitis, the most common form of Eczema.
2. Environmental Triggers
Various environmental elements can provoke or exacerbate eczema symptoms. These include:
- Allergens: Pollens, pet dander, and dust mites can cause allergic reactions leading to flare-ups.
- Irritants: Soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics may irritate the skin and worsen the condition.
- Climate Conditions: Extremes in temperature and humidity levels can destabilize the skin's barrier function, resulting in increased dryness and irritation.
3. Stress
Psychological stress is known to trigger or worsen eczema symptoms, particularly in conditions like neurodermatitis.
Recognizing these common causes helps tailor treatment strategies to minimize exposure and manage symptoms effectively.
Treatment Options for Managing Eczema Effectively
1. Topical Treatments: Emollients & Steroids
Treating Eczema effectively often begins with topical treatments, where emollients and steroids play a crucial role in managing symptoms.
Emollients for Eczema Management
- Function: Emollients are moisturizers that help to hydrate the skin, creating a barrier that locks in moisture and protects against external irritants.
- Application: Ideally applied immediately after bathing to maximize moisture retention. They can be used several times a day as needed.
- Types: Available in various forms such as creams, lotions, ointments, and gels. Selection depends on the severity of the Eczema and personal preference.
Steroids for Inflammation Control
- Purpose: Topical corticosteroids reduce inflammation and itching by suppressing the immune response at the site of application.
- Strengths: Available in different strengths, from mild to potent. Typically, milder versions are prescribed for sensitive areas like the face, while stronger ones may be used for more severe flare-ups on tougher skin surfaces.
- Usage Guidelines: It is crucial to follow medical advice regarding frequency and duration of use to avoid potential side effects like skin thinning.
Topical treatments offer a targeted approach to managing eczema symptoms. Regular use of emollients can prevent flare-ups by maintaining skin hydration, while corticosteroids provide relief during active inflammation. Understanding when and how to use these treatments can significantly improve quality of life for those dealing with Eczema.
2. Phototherapy: Light-Based Treatment for Eczema
Phototherapy, a light-based treatment, is often employed for managing various types of Eczema. It involves exposing the skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision. This method can help reduce inflammation and itchiness by slowing down the rapid growth of skin cells. There are different types of phototherapy, including:
- UVB Therapy: Utilizes UVB light, effective for treating widespread Eczema.
- PUVA Therapy: Combines UVA light with psoralen, a medication that sensitizes the skin to light.
Choosing the right phototherapy option depends on individual needs and specific eczema causes.
3. Lifestyle Changes: Managing Triggers & Keeping Skin Hydrated
Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing Eczema effectively. Identifying and avoiding triggers is key to minimizing flare-ups. Common triggers include:
- Environmental factors: Pollutants, allergens, and temperature extremes.
- Dietary influences: Certain foods may worsen symptoms for some individuals.
- Stress management: Techniques like meditation or yoga can help reduce stress-related flare-ups.
Hydration is vital, as keeping the skin moist helps maintain its barrier function. Using emollients for eczema management regularly softens the skin and prevents dryness. Personalized treatment approaches ensure strategies align with individual needs, enhancing overall eczema care.
Conclusion: Embracing Comprehensive Care for Eczema Management
Understanding the types of Eczema and their causes is crucial in managing Eczema effectively. Whether dealing with atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, or other forms, acknowledging each condition's unique triggers and symptoms can guide tailored treatment strategies.
Key strategies for effective management include:
- Identifying Triggers: Recognizing specific allergens or irritants that lead to flare-ups.
- Implementing Lifestyle Changes: Adopting habits like moisturizing regularly and maintaining a stress-free environment.
- Exploring Treatment Options: Utilizing topical treatments, phototherapy, and other medical interventions as recommended by healthcare professionals.
By embracing a comprehensive care approach that combines knowledge, proactive management, and appropriate treatments, individuals can significantly alleviate symptoms and enhance their quality of life. Always consult with dermatology experts to determine the most suitable plan tailored to your needs.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is Eczema?
Eczema is a common skin condition characterized by inflammation, leading to symptoms such as itchy and irritated skin.
What are the different types of Eczema?
The different types of Eczema include Atopic Dermatitis (Atopic Eczema), Contact Dermatitis (Allergic & Irritant), Dyshidrotic Eczema (Pompholyx), Nummular Eczema (Discoid Eczema), Seborrheic Dermatitis, Neurodermatitis (Lichen Simplex Chronicus), and Stasis Dermatitis (Venous Eczema).
What causes Atopic Dermatitis?
Understanding the causes of atopic dermatitis is essential for effective management. It can be triggered by genetic factors, environmental triggers, and psychological stress.
How is Nummular Eczema diagnosed?
Nummular Eczema is commonly mistaken for ringworm due to its appearance. A healthcare provider will typically diagnose it based on the characteristic symptoms and appearance of the skin.
What treatment options are available for managing Eczema?
Treatment options for managing Eczema effectively include topical treatments like emollients and steroids, phototherapy, and lifestyle changes aimed at managing triggers and keeping the skin hydrated.
What are common triggers for Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Understanding the triggers of seborrheic dermatitis can aid in management. Common triggers include stress, hormonal changes, weather conditions, and certain skin care products.