Scabies vs. Eczema: 5 Key Differences and Pictures to Help You Identify

Introduction
Red, itchy skin can signal various conditions, but two common culprits stand out: eczema and scabies. While these conditions share similar symptoms, they require vastly different treatments.
Eczema affects 31.6 million Americans, causing chronic dry, itchy patches that flare up periodically. This non-contagious condition stems from genetic factors and an overactive immune system.
Scabies, a highly contagious skin infestation, impacts over 200 million people worldwide. Microscopic mites burrow into your skin, triggering intense itching and distinctive rash patterns.
Distinguishing between these conditions is crucial for effective treatment:
- A misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective treatments
- Delayed scabies treatment risks spreading the infestation to others
- Wrong treatment approaches might worsen existing symptoms
This guide walks you through 5 key differences between eczema and scabies, complete with detailed pictures to help you identify each condition. You'll learn about their unique characteristics, typical symptoms, and specific body areas affected - essential knowledge for seeking appropriate medical care.
Understanding Eczema and Scabies
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, affects 31.6 million Americans - roughly 10% of the population. This chronic skin condition creates persistent inflammation and irritation, making it a long-term health concern for many individuals. For those suffering from chronic hand eczema, the impact on daily life can be especially challenging.
Scabies presents a different challenge as a highly contagious skin infestation. The condition affects over 200 million people worldwide, caused by microscopic Sarcoptes scabiei mites that burrow into the skin's surface. Scabies is not only uncomfortable but also requires careful management to prevent its spread.
Distinct Symptoms
Eczema Symptoms:
- Dry, scaly patches of skin
- Persistent itching
- Skin discolouration ranging from:
- Red to purple
- Grey to brown
- Ashen appearance
- Rough, leathery skin texture
- Raised bumps that may weep fluid
Scabies Symptoms:
- Intense itching that worsens at night
- Thin, irregular tracks where mites burrow
- Small pimples or blisters
- Crusty, scaly patches in severe cases
- Rash patterns in skin folds
Root Causes
Eczema develops from:
- An overactive immune system response
- Genetic mutations affecting skin barrier function
- Environmental triggers
- Allergic reactions
- Stress factors
Scabies stems from:
- Direct skin-to-skin contact with infected persons
- Sarcoptes scabiei mite infestation
- Sharing contaminated items like:
- Bedding
- Clothing
- Personal items
Treatment Approaches
Eczema Management:
- Regular use of moisturisers
- Topical corticosteroids
- Immunosuppressant medications
- Trigger avoidance strategies
- Lifestyle modifications
Scabies Treatment:
- Prescription scabicides
- Permethrin cream applications
- Oral ivermectin for severe cases
- Treatment of all close contacts
- Decontamination of personal items
Key Differences Between Eczema and Scabies You Need to Know
Understanding the distinct characteristics between eczema and scabies helps you identify these conditions accurately. Here are five critical differences you need to know:
1. Contagious Nature
- Eczema is not contagious - you can't catch it from someone else or spread it to others
- Scabies spreads rapidly through direct skin-to-skin contact or sharing personal items like bedding and clothing
2. Root Causes
- Eczema stems from genetic factors affecting your skin barrier function and an overactive immune system
- Scabies results from an infestation of microscopic Sarcoptes scabiei mites that burrow into your skin and lay eggs, similar to the cause of sarcoptic mange in canines
3. Symptom Characteristics
- Eczema creates:
- Mild to moderate itching
- Dry, scaly patches
- Skin discolouration varying from red to purple or brown
- Scabies produces:
- Severe itching that intensifies at night
- Distinctive burrow tracks under the skin
- Small, pimple-like bumps or blisters
- Crusty, scaly patches in severe cases
4. Affected Body Areas
- Eczema typically appears on:
- Neck and face
- Inner elbows
- Behind knees
- Hands and feet
- Scabies commonly affects:
- Finger webbing
- Wrist and elbow creases
- Waistline
- Genital area
- Breasts and buttocks
5. Diagnostic Approaches
- Eczema diagnosis involves:
- Clinical examination
- Review of medical history
- Allergy testing when needed
- Scabies diagnosis requires:
- Microscopic examination of skin scrapings
- Identification of burrow patterns
- Assessment of close contacts
- Confirmation of mite presence
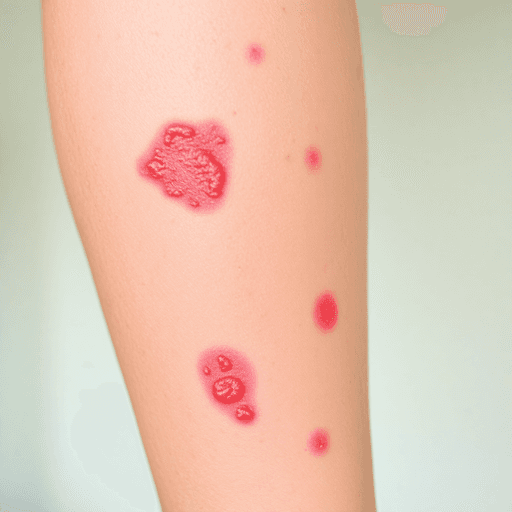
Visual Identification Guide: Pictures to Help You Differentiate Between Eczema and Scabies Effectively
Visual recognition plays a crucial role in identifying skin conditions accurately. Let's examine the distinctive visual characteristics of both eczema and scabies.
Identifying Eczema Through Images
- Red to brownish-grey patches
- Dry, cracked, or scaly skin
- Small raised bumps that may leak fluid
- Thickened skin with a leathery texture
- Symmetrical distribution on both sides of the body
Identifying Scabies Through Images
- Thin, irregular burrow tracks (silvery lines)
- Tiny blisters or bumps in a line
- Reddish-brown nodules
- S-shaped or zigzag patterns
- Crusty, scaly areas in severe cases
Key Visual Differences to Look For
- Pattern: Eczema shows patchy distribution; scabies displays linear tracks
- Texture: Eczema appears dry and scaly; scabies shows raised burrow lines
- Colour: Eczema ranges from red to grey; scabies presents as pink to reddish-brown
- Distribution: Eczema favours exposed areas; scabies targets hidden skin folds
Professional Tip: While these visual guides serve as helpful references, skin conditions can vary significantly between individuals. Proper medical diagnosis remains essential for accurate identification and treatment.
Conclusion
Distinguishing between eczema and scabies is crucial for effective treatment. These conditions require different approaches - eczema needs long-term management through moisturisers, corticosteroids and trigger avoidance, whilst scabies demands immediate treatment with scabicides and simultaneous treatment of close contacts.
A proper diagnosis from a qualified healthcare provider ensures you receive the right treatment plan. Watch for these key identifiers:
- Eczema: Non-contagious, genetic factors, dry patches in specific areas
- Scabies: Highly contagious, caused by mites, intense night-time itching
Armed with the knowledge of their distinct characteristics, you're better equipped to spot potential symptoms and seek appropriate medical attention. Remember - early identification leads to faster relief and prevents complications or spread to others.
FAQs
What are the main differences between eczema and scabies?
Eczema is a non-contagious chronic skin condition often caused by an overactive immune system and genetic factors, while scabies is a contagious condition caused by the infestation of the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. Key differences include their contagious nature, underlying causes, symptom intensity, affected body areas, and diagnosis methods.
How can I identify whether I have eczema or scabies?
Identification can be aided by understanding symptoms: eczema typically presents as dry, itchy skin with discoloration, while scabies causes intense itching that worsens at night along with rashes that may have bumps or crusts. Visual aids in the form of pictures can also help differentiate between the two conditions.
What are the common treatment options for eczema?
Common treatments for eczema include moisturizers to hydrate the skin, corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, immunosuppressants for severe cases, and avoiding known triggers that may exacerbate symptoms.
Is scabies contagious?
Yes, scabies is highly contagious and can spread through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infested person or through sharing personal items like clothing or bedding. It is crucial to treat close contacts to prevent further spread.
What are the common symptoms of eczema?
Symptoms of eczema include dry and itchy skin, which may appear discolored in red, purple, gray, brown, or ashen tones. The condition often leads to flare-ups that can be uncomfortable and persistent.
How is scabies diagnosed?
Scabies is diagnosed primarily through clinical examination by a healthcare professional. In some cases, microscopic examination of skin scrapings may be required to confirm the presence of mites or their eggs.