Does Atopic Dermatitis Improve with Age?

Introduction
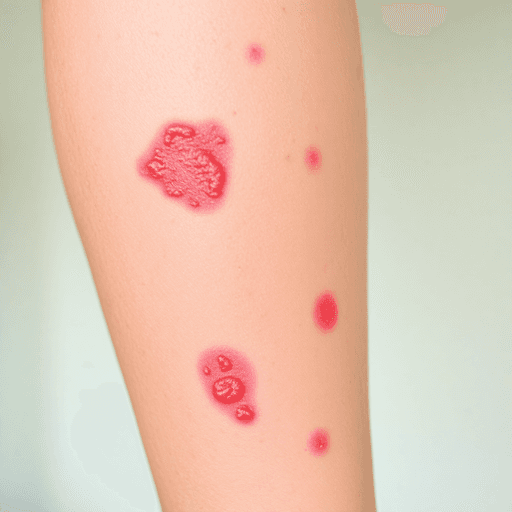
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a long-lasting skin condition that causes itchy, dry, and scaly skin. It usually starts in childhood and can greatly affect daily life. Many people believe that eczema symptoms get better with age, but this isn't true for everyone. While some individuals find relief as they grow older, others still struggle with the condition in adulthood.
This article aims to answer an important question: does atopic dermatitis improve as you get older? By understanding the factors that influence changes in symptoms over the years, we can gain valuable insights into managing this condition.
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, presents a range of symptoms that can significantly affect daily life. Common symptoms include:
- Itchy skin, often leading to intense scratching
- Dryness and scaling of the affected areas
- Red, inflamed patches that may ooze or crust over time
- Thickened skin from prolonged scratching
These symptoms highlight the importance of understanding the underlying factors contributing to eczema. The skin barrier plays a crucial role in this condition. When the barrier is compromised, it leads to increased water loss and makes the skin more susceptible to irritants, which worsens flare-ups.
Allergens and irritants have a significant impact on individuals with atopic dermatitis. Substances like soaps, detergents, pollen, and certain foods can trigger reactions. Even emotional stress can act as an internal trigger, causing heightened sensitivity and flare-ups.
It is essential to address these factors in order to effectively manage eczema. By focusing on strengthening the skin barrier and avoiding known triggers, individuals can gain better control over their symptoms and reduce the frequency of flare-ups.
The Age Factor in Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, often raises the question: does atopic dermatitis improve with age? It is a well-observed phenomenon that many individuals experience changes in their symptoms as they grow older. Yet, not everyone encounters this improvement uniformly.
Improvement Rates in Children vs. Adults
Statistics reveal that around 60% of children with early-onset atopic dermatitis see significant symptom resolution by the age of 12. This data, supported by research published in journals such as the British Journal of Dermatology, highlights a hopeful narrative for young sufferers. However, adults present a contrasting picture. For many, symptoms persist into adulthood and can sometimes lead to what is termed adult-onset eczema.
Adult-Onset Eczema: Treatment and Management
Adult-onset eczema presents unique challenges in treatment and management. Unlike childhood cases where skin might have a chance to heal over time, adult instances may require more targeted interventions. This condition can develop suddenly due to factors such as stress, hormonal changes, or exposure to new allergens.
Dr. Anna De Benedetto from the University of Florida College of Medicine emphasises personalised care strategies tailored to adult patients. The complexity of managing eczema in adults stems from the persistent nature of triggers and individual lifestyle factors contributing to flare-ups.
Factors Influencing Eczema Improvement or Persistence
Several elements play pivotal roles in determining whether eczema improves or persists:
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history significantly influences the likelihood of experiencing prolonged symptoms.
- Environmental Exposure: Continued exposure to irritants and allergens can exacerbate conditions.
- Lifestyle Choices: Diet, stress levels, and overall health contribute to symptom management.
- Skin Care Routine: Regular use of emollients and avoiding harsh skincare products can aid in reducing flare-ups.
Research Insights on Aging and Atopic Dermatitis
Studies continue to explore ageing's impact on eczema progression. Recent findings indicate that while some individuals see reduced inflammation over time, others face persistent issues due to skin barrier function degradation with age.
Dermatological studies frequently published in resources like the British Journal of Dermatology provide crucial insights into how ageing affects skin health. Some research suggests that ageing skin may become less responsive to traditional treatments but might benefit from newer therapeutic approaches.
This evolving understanding underscores the importance of ongoing dermatological research led by experts like Dr. Anna De Benedetto, who advocate for adaptive and innovative treatment plans that consider both age-related changes and individual patient needs.
The journey through life stages with atopic dermatitis varies widely among individuals. While some may find relief as they age, others continue seeking effective management strategies for persistent symptoms.
Eczema in Older Adults: A Different Manifestation
How Eczema Manifests Differently in Older Adults
Eczema in older adults often presents distinct characteristics compared to its manifestation in younger individuals. As the skin ages, it becomes thinner and less elastic, affecting how eczema symptoms appear and behave. This change can lead to a different experience of the condition, with symptoms possibly being more pronounced or persistent.
Older adults may notice that their skin is drier and more prone to irritation, which can worsen atopic dermatitis flare-ups. The condition might also display differently due to changes in the immune system associated with ageing, potentially leading to varied responses to allergens and irritants.
Common Types of Eczema Prevalent Among Seniors
Several specific types of eczema are more frequently observed in the elderly population:
- Varicose Eczema: Often linked with varicose veins, this type affects the lower legs and is characterised by itchy, inflamed skin that can become scaly or crusty. Poor circulation is a significant contributing factor.
- Asteatotic Eczema: Also known as xerotic eczema, this form occurs due to extremely dry skin. It typically manifests as cracked or fissured skin, commonly affecting arms and legs during colder months when humidity levels drop.
These types highlight how ageing can influence the presentation and severity of eczema, necessitating tailored management approaches.
Ageing, Skin Health, and Eczema Triggers for Seniors
Ageing brings about considerable changes in skin health, making it imperative to understand how these changes increase susceptibility to eczema:
- Decreased Sebum Production: With age, the sebaceous glands produce less oil, leading to drier skin that is more susceptible to irritation and cracking.
- Reduced Skin Barrier Function: The protective barrier of the skin weakens over time, allowing irritants and allergens easier access to deeper layers.
- Thinner Epidermis: The outermost layer of the skin becomes thinner with age, reducing its ability to retain moisture and protect against environmental factors.
Understanding these shifts helps explain why older adults might experience different triggers for eczema flare-ups compared to younger individuals. Common triggers include:
- Allergens: Environmental allergens such as dust mites or pet dander can aggravate symptoms due to compromised skin barriers.
- Stress: Emotional stressors often impact seniors differently than younger individuals due to various life circumstances, influencing eczema occurrence.
Grasping these nuances is essential for developing effective management strategies that cater specifically to the needs of older adults dealing with atopic dermatitis. For instance, utilising specialised products like eczema treatment creams can provide much-needed relief from symptoms.
Treatment Options for Eczema in Older Adults: Finding Relief at Any Age
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, presents unique challenges for older adults. With age, changes in skin physiology can worsen symptoms, requiring personalised management strategies. Understanding the intricacies of treating eczema in older adults is crucial to improve quality of life and reduce risks of social isolation.
Skincare Routines and Medications
Effective management of eczema in seniors often requires a multifaceted approach:
- Moisturising: Regular use of emollients helps in maintaining skin hydration. Older adults benefit from thick creams or ointments applied immediately after bathing to lock in moisture.
- Topical Treatments: Corticosteroid creams are a staple for reducing inflammation during flare-ups. Non-steroidal options like calcineurin inhibitors may also be recommended to limit steroid exposure.
- Antihistamines: These can alleviate severe itching, particularly helpful if sleep is disrupted by nighttime pruritus.
- Systemic Therapies: In cases where topical treatments are insufficient, systemic medications like biologics or oral corticosteroids might be considered, under close medical supervision.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Management Strategies to Consider
Adapting daily routines can significantly impact eczema management:
- Gentle Cleansing: Use mild, fragrance-free soaps to avoid irritating sensitive skin.
- Clothing Choices: Opt for soft, breathable fabrics such as cotton to reduce skin irritation.
- Humidity Control: Keeping indoor air moist with humidifiers can prevent skin from drying out during colder months.
Emotional Impact and Social Engagement
Living with eczema extends beyond physical discomfort; it can deeply affect emotional well-being. Social isolation becomes a risk as individuals might withdraw due to embarrassment or discomfort caused by visible symptoms.
- Understanding Emotional Challenges: The chronic nature of eczema can lead to frustration and low self-esteem. Encouraging open discussions about these feelings with family members or support groups promotes better mental health.
- Combatting Isolation:
- Social Activities: Engaging in community events or hobby groups keeps social connections strong.
- Support Networks: Joining support groups specifically for those dealing with chronic skin conditions provides a sense of belonging and shared understanding.
Maintaining an active social life not only improves emotional health but may also positively influence physical symptoms. Stress is a known trigger for eczema flare-ups; thus, reducing stress through social interaction can potentially lead to fewer outbreaks.
For older adults managing atopic dermatitis, the key lies in comprehensive care that addresses both physical symptoms and emotional well-being. By implementing effective treatment options and fostering social engagement, seniors can find relief and maintain a fulfilling lifestyle despite the challenges posed by eczema.
Conclusion: Embracing Hope and Seeking Help for Eczema Management Throughout Life's Stages
Atopic dermatitis can be a persistent companion throughout one's life, but understanding whether it improves with age can offer hope. If you wonder, "does atopic dermatitis improve as you get older?", it's essential to remember that each individual's journey is unique.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Does atopic dermatitis improve with age?
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, often raises the question of whether it improves with age. While many children experience significant improvement as they grow older, adult-onset eczema may present unique challenges and may not show the same improvement.
What are the differences in eczema improvement rates between children and adults?
Statistics reveal that around 60% of children with early-onset eczema see improvements as they age. In contrast, adults may face persistent symptoms or new onset of eczema, making their experience different from that of children.
What factors influence the improvement or persistence of eczema?
Several elements play pivotal roles in determining whether eczema improves or persists. These include genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, skincare routines, and lifestyle adjustments that can significantly impact management strategies.
How does ageing affect the manifestation of eczema in older adults?
Eczema in older adults often presents distinct characteristics compared to younger individuals. Commonly observed manifestations may include dryness, increased sensitivity, and a tendency for eczema to appear in different areas of the body.
What treatment options are available for managing eczema in older adults?
Effective management of eczema in seniors often requires a multifaceted approach, including topical medications, skincare routines tailored to ageing skin, and lifestyle adjustments aimed at minimising triggers while providing relief.
How can emotional health and social engagement be affected by living with eczema?
Living with eczema extends beyond physical discomfort; it can have significant emotional impacts. Individuals may experience anxiety or social withdrawal due to their condition, highlighting the importance of seeking support and engaging with others for overall well-being.
Seeking medical advice and developing personalised care strategies tailored to your specific needs is crucial. Whether you're experiencing flare-ups or seeking preventive measures, medical professionals can guide effective management practices. Don't hesitate to reach out for support in navigating the complexities of living with eczema at any stage of life.